| IN A NUTSHELL |
|
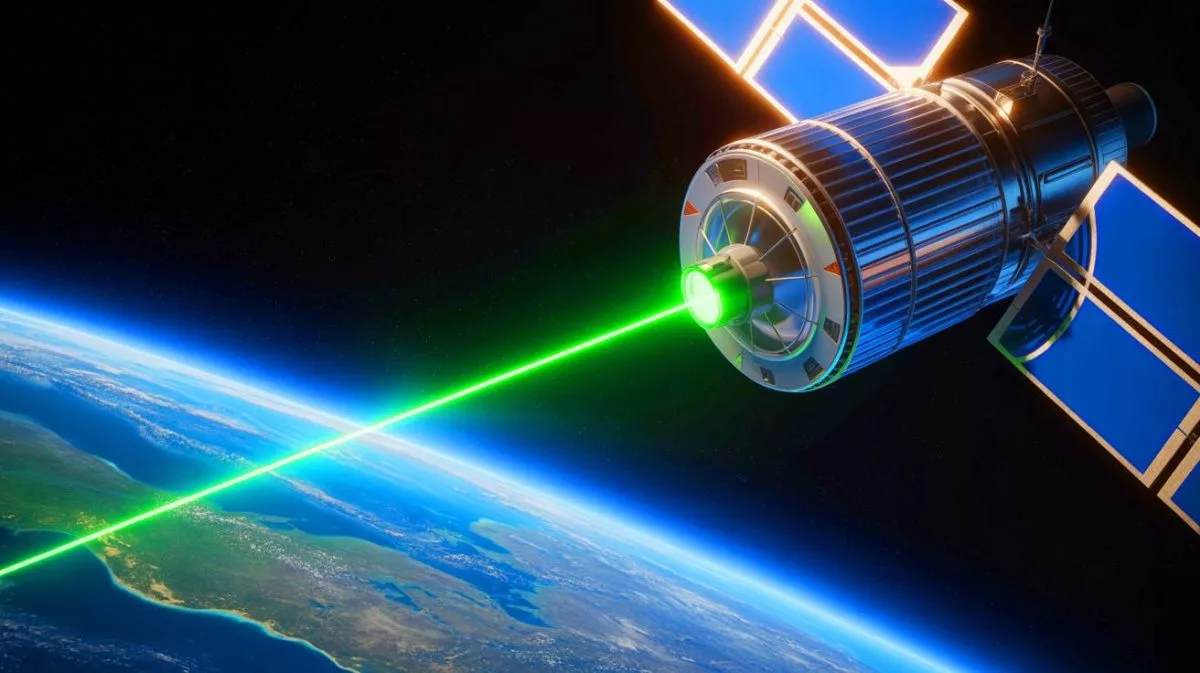
In a significant leap for satellite communication technology, Chinese scientists have developed an innovative laser-based data transmission method. This breakthrough involves a 2-watt laser capable of transmitting data at 1 Gbit/s from a distance of 22,369 miles. Remarkably, this speed is five times faster than the well-known Starlink satellites. The implications of this technology could be transformative, potentially revolutionizing future communication networks and research possibilities. As global reliance on rapid data transfer intensifies, such advancements highlight the potential for more efficient and far-reaching communication methods.
A Revolutionary Approach to Data Transmission
The new method developed by the Chinese researchers addresses a long-standing challenge in laser-based data transmission: atmospheric turbulence. This phenomenon disrupts the clarity of laser signals, making it difficult to maintain data integrity over long distances. Traditionally, two main techniques were used to combat this issue: adaptive optics (AO) and mode division reception (MDR). Adaptive optics work to sharpen distorted light, while MDR captures scattered signals. However, each method alone proved insufficient under severe turbulence conditions.
Under the guidance of Professor Wu Jian from Peking University of Posts and Telecommunications and Liu Chao from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, a synergistic approach combining AO and MDR was developed. This innovative combination effectively mitigates the limitations of each method, significantly enhancing data transmission reliability even in challenging atmospheric conditions. The synergy between AO and MDR represents a substantial advancement in satellite communication, offering a robust solution to previously insurmountable obstacles.
The Impressive Performance of the 2-Watt Laser
The implementation of a 2-watt laser, though seemingly modest in power, has resulted in extraordinary outcomes. Comparable to the light emitted by a small candle, this laser successfully transmits data at a remarkable speed of 1 Gbit/s. In contrast, Starlink satellites, operating at much lower altitudes of a few hundred miles, achieve maximum speeds of only several megabits per second. The new technology drastically surpasses this performance, operating effectively over a much greater distance of 22,369 miles.
The capability to transfer an HD movie from Shanghai to Los Angeles in under five seconds is nothing short of revolutionary. This advancement not only has the potential to transform how we exchange information but also opens up new applications in sectors such as telecommunications, research, and defense. The 2-watt laser’s performance exemplifies the significant advancements possible through the fusion of technological innovation and creativity.
Challenges of Atmospheric Turbulence
Atmospheric conditions pose a major challenge to laser-based data transmission from space. Turbulence in the Earth’s atmosphere can scatter light and significantly impair data quality. Previous global research efforts have struggled to fully overcome these issues. Atmospheric scattering causes light to disperse into extremely weak and blurred spots, complicating processing upon reaching the Earth’s surface.
The AO-MDR synergy proposed by Chinese scientists represents a significant breakthrough by minimizing the adverse effects of turbulence. This innovative method substantially improves the accuracy and reliability of data transmission. By combining technologies previously used independently, researchers have developed a solution that operates effectively under real-world conditions.
“Doctors Warn of Chaos”: China’s Pig Lung Transplant Stirs Global Medical Tensions
Implications for the Future of Communication Technology
The successful implementation of this technology could have profound implications for the future of communication. The ability to transmit large volumes of data quickly and reliably over vast distances may enable new applications and services previously deemed unfeasible. In remote or hard-to-reach areas, this technology could revolutionize access to high-speed internet connections.
Furthermore, the AO-MDR synergy opens new avenues for research and development. The capability to perform precise data transmissions under challenging conditions could be crucial in fields such as science and defense. The question remains how this technology will be further refined and utilized in the coming years to enhance and transform global communication.
The groundbreaking advancement in laser-based data transmission by Chinese scientists underscores the immense potential of technological innovation. These developments could fundamentally change how we communicate and exchange information. The central question remains: What other revolutionary technologies await discovery and implementation to further transform our world?
Did you like it? 4.4/5 (27)







Wow, 5 seconds for an HD movie? That’s faster than my microwave! 🍿
This is insane! A movie in 5 seconds? What else can they beam down? 🚀😲
How long before this tech becomes available commercially? Seems revolutionary!
How reliable is this laser tech in bad weather conditions like storms or heavy rain?
I hope they’re considering security implications. Fast data is great until it falls into the wrong hands.
I wonder how long it will take for this technology to become mainstream. Any guesses?
Does anyone else find it a bit scary that China is leading the charge in space tech? 🤔
Is it safe to have such powerful lasers beaming down to Earth? Sounds a bit risky. 😅
So Starlink is basically obsolete now? What will Elon Musk do about this?
Honestly, I’m skeptical. Sounds too good to be true. What’s the catch?
I’m curious about the cost of implementing such technology. Will it be affordable?