| IN A NUTSHELL |
|
In a groundbreaking move toward a more sustainable future, China has delivered the final components for the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER), often dubbed the “artificial sun.” This international project, situated in the south of France, aims to mimic the sun’s fusion process to revolutionize energy production. By potentially offering a clean and nearly inexhaustible energy source, ITER marks a significant step in reducing global dependence on fossil fuels.
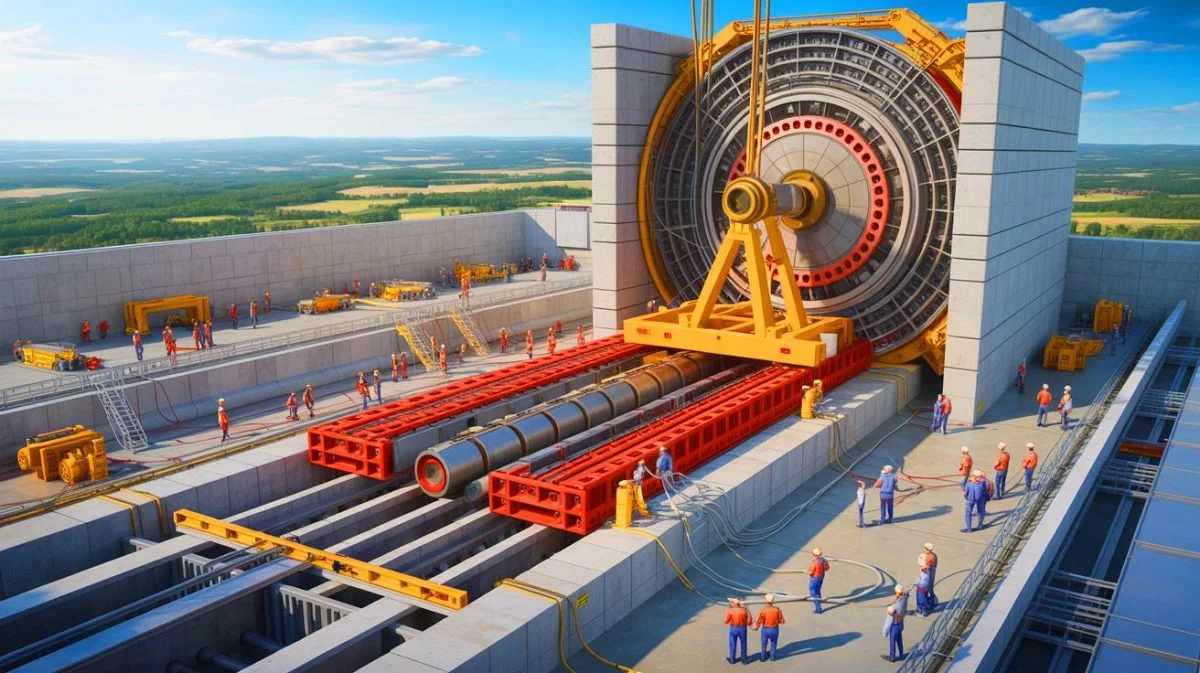
China Delivers Magnetic Feeder System for ITER
The recent delivery of the magnetic feeder system is a critical milestone in the ITER project. Developed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ Institute of Plasma Physics, this system is essential for the reactor’s operation. It supplies necessary energy and cooling to the reactor magnets, which are vital for sustaining fusion reactions. Moreover, it transmits crucial control signals and serves as a discharge channel to safely release stored magnet energy.
Weighing approximately 3,500 pounds, this magnetic feeder system is the most complex component China has contributed to ITER. This feat underscores China’s dedication to advancing global fusion research and demonstrates the collaborative spirit among the seven international partners involved in this project: the European Union, the United States, Japan, South Korea, India, and Russia. Together, they exemplify the global cooperation needed to address pressing energy challenges.
Inching Towards First Plasma
ITER is on the verge of achieving its first plasma, a landmark step in developing a large-scale fusion reactor capable of producing more energy than it consumes. This breakthrough, expected in the coming years, holds immense potential for providing a clean and limitless energy source.
China’s own fusion initiative, the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST), further demonstrates the viability of fusion energy. EAST recently set a record by maintaining a stable plasma loop for over 1,066 seconds, signifying progress in sustainable energy solutions. Such advancements bring us closer to a future powered by clean, fusion-based energy.
The Collaborative Effort Behind ITER
Launched in the mid-1980s, ITER is among the most ambitious scientific projects ever undertaken. With participation from key global players, the project’s estimated cost exceeds $25 billion, reflecting its immense scale and complexity. Despite these challenges, the potential benefits are substantial.
Fusion energy offers significant safety and environmental advantages. Unlike nuclear fission, fusion does not produce long-lived radioactive waste and emits zero greenhouse gases. Additionally, the risk of catastrophic accidents is much lower, making fusion a safer and more sustainable energy option for the future.
The Path Forward: Challenges and Opportunities
Despite promising progress, several challenges remain on the path to commercial fusion energy. Overcoming technical hurdles and scaling up the technology are essential to realizing fusion’s potential. However, the rewards justify these efforts, as fusion could provide a stable, reliable, and environmentally friendly energy source that meets the growing global demand without the disadvantages of current systems.
ITER’s collaborative model demonstrates how pooling resources and expertise can lead to breakthroughs impossible to achieve individually. Its success could pave the way for further international cooperation in addressing other global challenges, such as climate change and sustainable development.
As we stand on the brink of a new era in energy production, the world must decide: how will we embrace and integrate fusion technology into our existing infrastructure to ensure a sustainable future for generations to come?
Did you like it? 4.5/5 (21)







Wow, China really pulled off a game-changer! 🌏 Is this the start of a new energy era?
Fusion energy sounds amazing, but how long until it becomes a reality for everyday use?
Thank you for the detailed update! This is the kind of progress the world needs. 🙌
Is this really going to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels or is it just another big promise?
Why does it seem like China’s always ahead in these tech breakthroughs? 🤔
Can someone explain how this “artificial sun” works in simple terms?
Incredible! Hope this collaboration continues to thrive. 🌟