| IN A NUTSHELL |
|
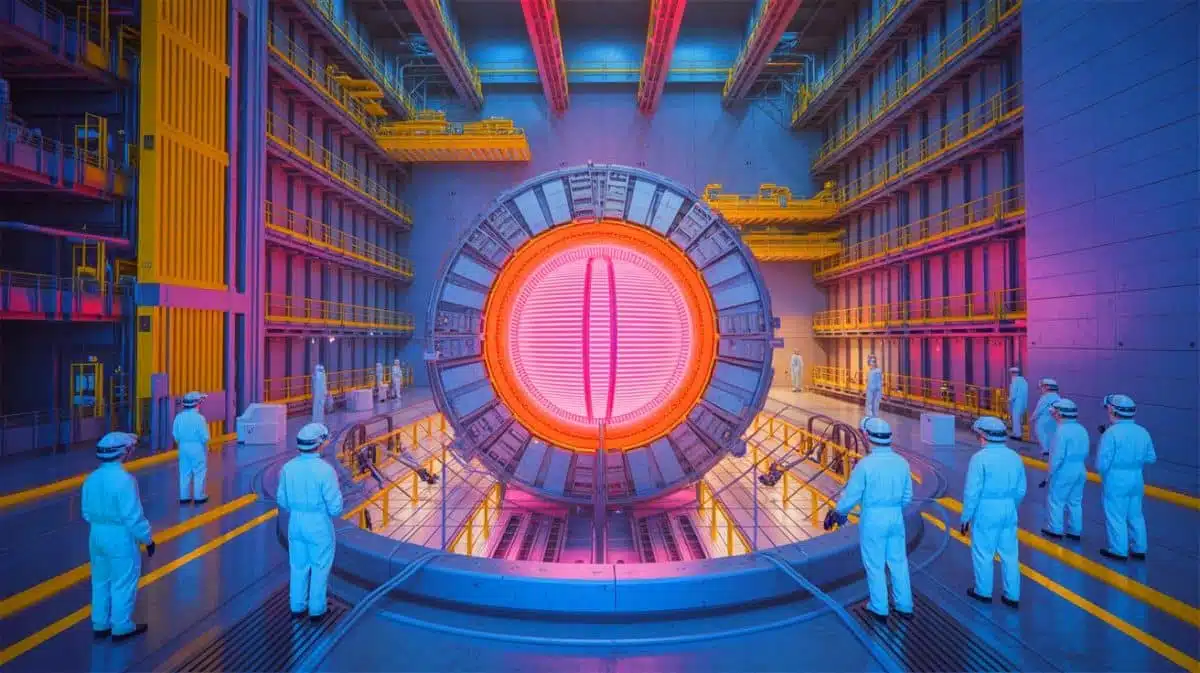
The International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) project, based in southern France, represents a collaborative scientific endeavor of unprecedented scale. Supported by over 30 countries, including the U.S., China, Japan, Russia, and the European Union, the project’s ultimate goal is to generate clean energy through nuclear fusion. The recent announcement that the project’s central solenoid, the world’s most powerful magnet, is ready for assembly marks a key milestone in this ambitious undertaking. This magnet is crucial for confining the super-hot plasma particles necessary for fusion, underscoring the intricate and challenging nature of creating energy by smashing atoms together at extraordinarily high temperatures.
The Role of the Central Solenoid in Nuclear Fusion
At the heart of the ITER project lies the central solenoid, a pivotal component needed to achieve nuclear fusion. This powerful magnet is designed to create an “invisible cage” that confines the super-hot plasma particles. These particles, when combined, release energy through the process of fusion. The central solenoid’s function is akin to a wine bottle; while the contents are what ultimately matter, a sturdy container is essential to hold them. Pietro Barabaschi, ITER’s Director General, emphasized this analogy, highlighting the indispensable role that the magnet plays in the fusion process. Originally slated for completion in 2021, the central solenoid faced several delays, reflecting the project’s complex challenges. Despite these setbacks, the completion and testing by the U.S. have set the stage for the assembly phase, marking a significant step forward in the ITER project’s timeline.
Overcoming Challenges and Delays
Like many large-scale scientific projects, ITER has faced its share of challenges. The project has been delayed by four years beyond its scheduled timeline, illustrating the intricate hurdles involved in such an ambitious endeavor. Charles Seife, a professor at New York University, pointed out the project’s troubled history, noting the significant delay after a decade of effort. However, according to Barabaschi, the crisis phase is now over, and construction is advancing at the fastest pace in the project’s history. The project is now on track to enter its start-up phase in 2033, when it is expected to begin generating plasma. This progress reflects the resilience and determination of the international team, demonstrating that even amidst geopolitical tensions, countries can unite towards a common scientific goal.
Global Cooperation and Cohesion
One of the remarkable aspects of the ITER project is its demonstration of international cooperation. Despite varying geopolitical landscapes, countries involved in ITER remain committed to its objectives. Barabaschi noted the strong cohesion among the nations involved, with no signs of withdrawal from any participating country. This unity is crucial for the project’s success, highlighting how global collaboration can advance scientific knowledge and technological innovation. The significance of such cooperation extends beyond the scientific realm, serving as a beacon of hope for international relations in a world often marked by division.
The Future of Fusion Energy
The potential of nuclear fusion as a source of clean energy has spurred interest and investment worldwide. Alongside ITER, numerous private start-ups are exploring the possibilities of commercial fusion reactors, with some claiming they could be operational within a decade. However, Barabaschi remains skeptical about the feasibility of achieving cost-effective fusion energy in such a short timeframe. While acknowledging the growth in fusion investment, he emphasized the need for patience and realistic expectations. The key question remains: can fusion be achieved in a manner that is both economically viable and scalable? Barabaschi’s cautious optimism reflects the complex interplay of scientific innovation and economic practicality that will shape the future of fusion energy.
As the ITER project continues to make strides, it serves as a testament to human ingenuity and the power of collaboration. The journey towards achieving sustainable fusion energy is fraught with challenges but offers the promise of a cleaner, more sustainable future. As we look to the future, the question remains: how will the lessons learned from ITER shape the next generation of energy solutions and global cooperation?
Did you like it? 4.5/5 (24)








Wow, this sounds like science fiction! How soon can we expect fusion power in our homes? 🔮
Another four-year delay? What’s causing all these setbacks? 🤔
Great article! It’s amazing what international cooperation can achieve. Thank you for the insights!
The ITER project sounds promising, but what are the potential risks of nuclear fusion?
Isn’t this similar to what the sun does? How do scientists replicate such conditions on Earth?
I hope this really leads to carbon-free power. Excited for the future! 🌍
When talking about clean energy, shouldn’t we focus on wind and solar instead?
Does anyone else feel like this is too good to be true? 😅
Thank you for the detailed information. This is a game-changer!