| IN A NUTSHELL |
|
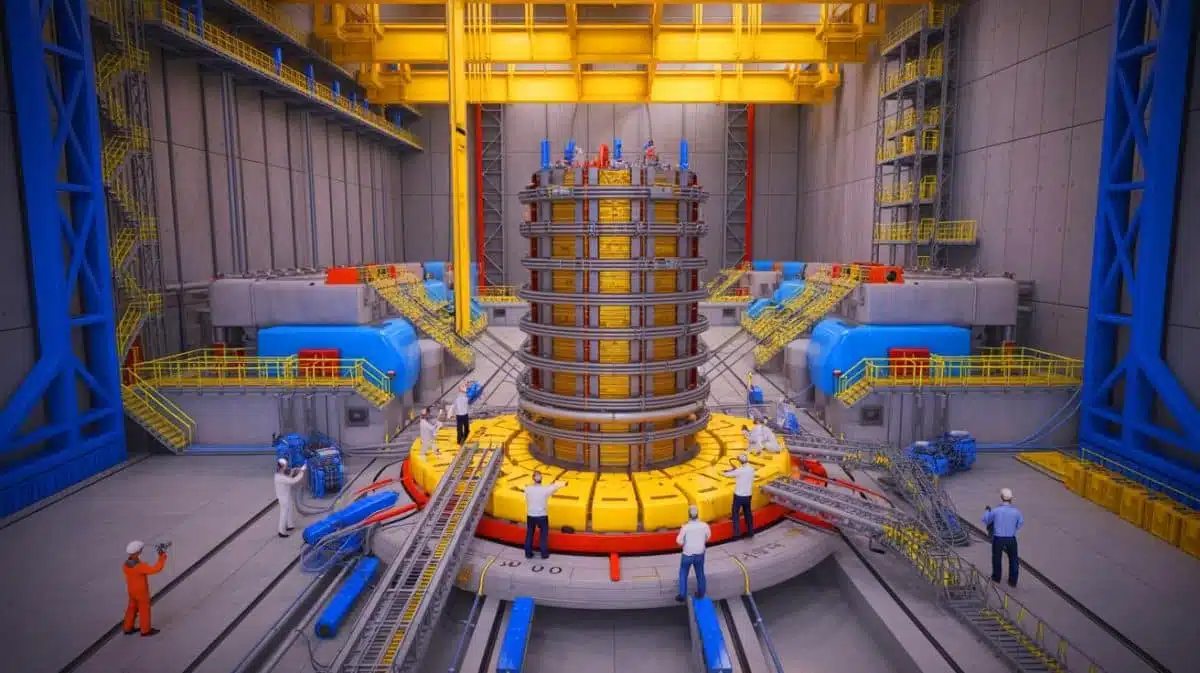
The arrival of the final shipment of components for the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) from China marks a pivotal moment in the quest for sustainable energy. Known as the “artificial sun”, ITER aims to revolutionize energy production by replicating the fusion process of the sun. Located in the south of France, this ambitious project is a testament to international collaboration and commitment to reducing reliance on fossil fuels. The promise of clean, nearly limitless power from nuclear fusion could transform energy systems worldwide, highlighting the importance of ITER’s progress.
China Delivers Magnetic Feeder System for ITER
The recent delivery of the magnetic feeder system from China represents a significant advancement in ITER’s construction. Developed by the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ Institute of Plasma Physics (ASIPP), this system is crucial for the reactor’s operation. It plays a key role in delivering energy and cooling media to the fusion reactor magnets, which are essential for maintaining fusion reactions. Additionally, it transmits vital control signals and provides a discharge channel for safely releasing stored magnet energy.
Weighing approximately 3,527 pounds, this complex system is the most intricate ITER procurement package from China. This milestone underscores China’s dedication to advancing fusion research on a global scale. The project is a collaborative effort, with funding from a consortium of nations including the European Union, the United States, Japan, South Korea, India, and Russia. This joint venture highlights the collective spirit required to address the global energy challenges of our era.
Inching Towards First Plasma
The ITER project is nearing a significant breakthrough as it prepares to achieve its first plasma, anticipated in the coming years. Creating the first plasma is a crucial step towards developing a large-scale fusion reactor capable of generating more energy than it consumes. The potential of fusion technology is immense, offering a path to a clean, limitless energy source.
China’s Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) project recently demonstrated the viability of fusion by maintaining a stable plasma loop for over 1,066 seconds. This achievement exemplifies the progress in fusion energy research and brings us closer to realizing a future powered by clean, fusion-based energy. The success of these projects paves the way for significant advancements in sustainable energy production.
The Collaborative Effort Behind ITER
Initiated in the mid-1980s, ITER is one of the most ambitious scientific projects undertaken, involving seven major partners: the US, Russia, South Korea, Japan, China, India, and the European Union. With an estimated cost exceeding $25 billion, the project’s scale and complexity are immense. Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of ITER are substantial.
Fusion energy offers distinct advantages over traditional energy sources, including safety and environmental benefits. Unlike nuclear fission, fusion does not produce long-lived radioactive waste and emits zero greenhouse gases. Furthermore, the risk of catastrophic accidents is significantly lower, making it a safer, more sustainable option for future energy production. This collaborative effort is crucial for achieving breakthroughs in fusion technology and addressing global energy needs.
The Path Forward: Challenges and Opportunities
While ITER and other fusion projects show remarkable promise, numerous challenges remain. Achieving commercial fusion energy requires overcoming technical obstacles and scaling up the technology. However, the potential rewards are immense. Fusion could provide a stable, reliable, and environmentally friendly energy source to meet growing global demands without the negative impacts of current energy systems.
The collaboration demonstrated in ITER serves as a model for future scientific endeavors. By sharing resources, expertise, and knowledge, countries can achieve breakthroughs that would be impossible individually. The success of ITER could pave the way for further international cooperation on other global challenges, such as climate change and sustainable development. As we stand on the cusp of a new era in energy production, the question remains: how will the world embrace and integrate fusion technology into our existing infrastructure to ensure a sustainable future for coming generations?
Did you like it? 4.4/5 (27)








Wow, China’s really stepping up its game in the energy sector! 🚀
Isn’t it risky to rely so much on one country for critical tech components?
Finally, a step towards cleaner energy! Thank you, China! 🙌
But what about the cost? $25 billion isn’t exactly pocket change.
Will this actually lead to cheaper electricity bills in the future? 🤔
Can someone explain what a “magnetic feeder system” does exactly?
Why does it feel like we’re always “nearing a breakthrough” with fusion? 😅
Is fusion energy safe? I’ve heard it’s better than fission.
China’s commitment is impressive, but how do other countries feel about this?
Great article! I’m excited to see where this leads in 10 years.
What are the environmental impacts of building ITER?
ITER sounds like a sci-fi movie plot! Can’t wait to see the “artificial sun”! 🌞
How does fusion compare to renewable sources like solar and wind?
Thank you for this in-depth piece. Very informative! 👍
Are there any geopolitical risks involved with China’s involvement?
So when can we expect this technology to be available commercially?
In decades
Hope this doesn’t lead to another cold war over energy resources! 😬
Fusion energy sounds promising, but I’ve heard that before… 🤷♂️
Why is the US involved if China is doing all the work?
Isn’t there a risk of accidents with fusion reactors?
Finally, a step towards reducing our carbon footprint. Thanks, ITER! 🌍
How many jobs will this project create globally?
The scale of this project is mind-boggling! 🤯
When’s the next update on ITER’s progress expected?
Why haven’t we invested more in fusion energy sooner?
Let’s hope this doesn’t become another political tool. 🤞
What role do private companies play in the ITER project?
Is the project’s timeline realistic given the challenges?
How does ITER plan to deal with technical obstacles?
China’s involvement is a game-changer. But in a good way? 🤔
Does the project have any backup plans if things go wrong?
Fusion energy = future! Let’s make it happen! 🚀
What can individuals do to support fusion energy research?
Are there any documentaries about the ITER project?